4 Enterprise Uses for VR in the Automotive Industry



4 Enterprise Uses for VR in the Automotive Industry
The use of VR in the automotive industry isn’t new.
Ford has been using VR to various degrees to design vehicles since the year 2000. But vehicle design is only one of the many ways that automotive companies have been using VR. Other enterprise use cases include training employees, customer research and marketing.
Since VR has been a standard in the automotive space for decades, it's important to consider how you can get an edge over your competitors. The best way is to track the right metrics so you can receive meaningful insights about your VR implementation.
In this blog, we'll cover 4 ways enterprises are using VR in the automotive industry to improve business processes.
Vehicle Prototyping

Image via: Ford
This is a picture of Michael Smith, a Design Manager at Ford who built a 3D render of a race car in 40 hours using Gravity Sketch on the Unreal Engine. When asked how long it would’ve taken using a traditional method like 2D sketching or CAD software. He replied that it would take a few months at least.
Prototyping in VR is cheaper, faster and more effective than other methods. There are a few reasons for this:
- Virtual prototypes can be changed on the fly based on feedback
- Feedback can be incorporated much sooner in the design stage.
- Constant iterations can be made at little to no extra cost.
Designers have the ability to manipulate and examine virtual prototypes from any angle and at any scale. Room scale VR provides a new perspective because it moves designers from 2D to 3D space. This lets them evaluate and make changes to the vehicle immediately.
Customer Research

Image via: Forbes
There’s a lot of risk involved in releasing a new vehicle.
Customer behavior is always changing and companies must stay ahead of their competition. It’s important to do customer research as early into the design process as possible.
VR makes it cheaper to make changes based on customer validation and feedback. By being more responsive to feedback, companies can better design customer centric vehicles.
"The way that people perceive things can be very subtle,” said Elizabeth Baron, Immersive Realities Technical Specialist at Ford. To test these perceptions, Ford simulated “bright daylight or a cloudy day, and night time, to see how it would look" in those conditions.

By tracking VR specific metrics such as:
- Biometrics
- User Position
- Eye Tracking
These metrics will help companies understand their customers better. For example, it’s important to observe how customers examine vehicles. Which features are they noticing first? What draws their attention? How long did they look at each detail?
Vehicle features be changed to the customer’s liking. Different trims and colors can be tested to see how they’re received. Companies can also test the interior of the vehicle to assess how intuitive the layout is. Did customers have trouble finding the placement of the volume control?
These tests can be combined with biometrics to give automotive companies a wealth of data to reduce risk, lower cost, and improve the success of new vehicles.
Employee Training

Image via: Unity
Through our own studies, we found that training in VR improved knowledge retention of skilled workers by 57% compared to video or text. People learn much better by doing than by observing. Practicing tasks in VR helps people get a better feel for the motions required.
To better understand how to improve employee performance, it’s necessary to measure training effectiveness. For example, Ford measured body stress and comfort in VR to make sure employees weren’t risking injury when assembling larger vehicles and were able to reduce the injury rate by 70%.
Below are a few examples of what to measure:
- What captures trainee attention
- Task completion speed
- User compliance rates
Companies can improve VR training effectiveness and efficiency by fixing bottlenecks in the simulation.
Marketing
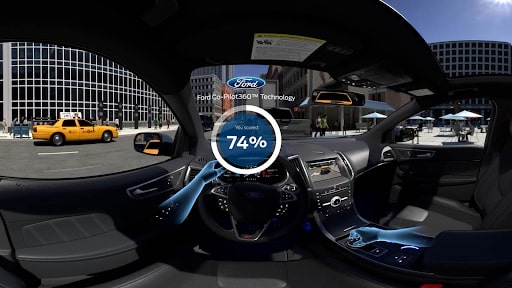
Image via: Groove Jones
The experiences delivered through VR are much more memorable compared to traditional media platforms. Omnivert found that Immersive ads increased CTR by 300% compared to 2D ads.
The automotive industry is especially suited for VR because of how well it simulates driving. Once again, Ford is a trailblazer in VR implementation. In 2019, they created an experience to showcase their Co-Pilot360 technology. Co-Pilot360 is a safety system that auto detects hazards around the vehicle. Ford wanted to show people the types of hazards they’re missing while on the road.
Customers used their controllers to react to hazards and were given a score at the end of the simulation. By measuring user gaze, Ford assessed what they noticed and what they missed.
Using VR in your Marketing campaigns will provide customers with experiences they won’t forget.
Design Better Vehicles With Analytics
In this blog we’ve discussed 4 enterprise use cases for VR. But, implementing VR is only half of the equation. You need measurable results to prove business results and ROI.
This is where Cognitive3D comes in.
We make it easy for you to start using VR analytics.
Our platform is headset agnostic and it supports a number of software engines including Unity, Unreal, C++ and JS.
This means you can simply install our SDK and connect your headset to receive analytics.